Recent Publications
As the Bay Area’s trade and investment with Europe grows, Ireland occupies a unique position as a platform and technology bridge between the US and Europe. It has successfully combined targeted economic strategies with talent and innovation, creating a highly competitive European base for Bay Area and other US companies. The Bay Area’s relationship with Ireland reflects a mutually beneficial economic alignment but also deep historical roots, with 2023 marking the 90th anniversary of Ireland’s diplomatic presence in San Francisco. Through its large Irish community, active engagement by the Irish Government, and strong economic and cultural linkages, the San Francisco Bay Area serves as a key connector between Ireland and the United States.
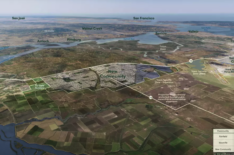
Read More in the Summary »The East Solano Plan seeks to create a new, mixed-use community at the heart of the Northern California Megaregion with homes, businesses, and civic uses organized into medium-density neighborhoods. At full build out, the plan has room for 400,000 people. The plan includes a commitment to bring 15,000 jobs to Solano County in the first phase of development, along with $500 million in community benefits such as downpayment assistance for Solano County residents and a $200 million fund to invest in revitalizing existing downtowns throughout Solano County. At full build out, these numbers increase to $4 billion in community benefits and $800 million for Solano County downtowns.
Read More in the Summary »Without intervention, wildfires will continue to threaten homes, create economic costs, and jeopardize the health of the state’s residents. A variety of Federal, State and local programs, grants, and initiatives are advancing, however public-sector programs alone are unlikely to ever reach the scale necessary to completely mitigate the threat. It is therefore essential to co-develop programs and initiatives to leverage the resources within the private sector.
Read More in the Summary »This conversation took place at a December 2023 symposium jointly sponsored by the Bay Area Council Economic Institute, the Stanford Center for China’s Economy and Institutions (SCCEI) and the Shenzhen-based China Development Institute (CDI) on where, despite the obstacles, opportunities can still be found to build business and economic ties between the U.S. and China.
Read More in the Summary »To unlock the economic potential of achieving racial equity, the Bay Area’s policymakers, businesses, nonprofit institutions, community groups, and other critical stakeholders must become not only a voice for change, but the actors of change. To truly bridge the deeply entrenched divides will require new policies, new investments, and new strategies. Most importantly, it requires racial equity to rise to the forefront of decisions made by business and government. Racial equity will not be achieved by a single policy or investment; it instead is a goal that requires numerous steps to break down biases—both conscious and unconscious—and to fundamentally restructure how economic decisions are made.
Read More in the Summary »This conversation summarizes one of fourteen forums organized by the Bay Area Council during APEC (November 13-17, 2023). Designed to introduce global partners to the startup and innovation environment in the San Francisco/Silicon Valley Bay Area, it brought together leaders from venture capital, venture finance, accelerators and universities for a discussion of Silicon Valley’s origins and of key trends shaping its present and future.
Read More in the Summary »Multilingual Learning Programs hold immense potential to transform California’s education system and prepare
student to thrive in an increasingly connected world. By addressing the current challenges and implementing the
suggested policy recommendations, California can create a robust framework for MLL programs that will benefit
students, teachers, businesses, families, and communities, while fostering a more inclusive, diverse, and prosperous
state.
Luxembourg’s position as a business-friendly European economy suggests a range of opportunities for investment and other partnerships with Bay Area and other U.S. companies.
Read More in the Summary »The war in Ukraine and multidimensional challenges from China have brought to the fore the need for the transatlantic partners to increase their collaboration and coordination as a way to reestablish geopolitical equilibrium and address the challenges posed by autocratic techno-nationalism.
Read More in the Summary »Enhanced communications infrastructure across California—especially for wireless connectivity—can play a role in ensuring broadband access for all. This infrastructure is also the backbone that allows advancements in technology to thrive. Without consistent investment in communications infrastructure across California, a new issue is emerging as technologies advance: an innovation gap. With more and more daily activities requiring a robust digital presence, those areas that fall behind on infrastructure investment will also risk creating a new opportunity gap for businesses and residents that are unable to access the latest technologies.
Read More in the Summary »Synergies between the Bay Area and India’s robust innovation ecosystem suggest a wide range of opportunities for collaboration. Key thematic areas include defense, critical and emerging technologies (enabled by iCET), standards, state-level collaboration on climate and energy, cross-national support for startups, AI and digital development, skilled immigration, trade, and supply chain integration.
Read More in the Summary »